はじめに
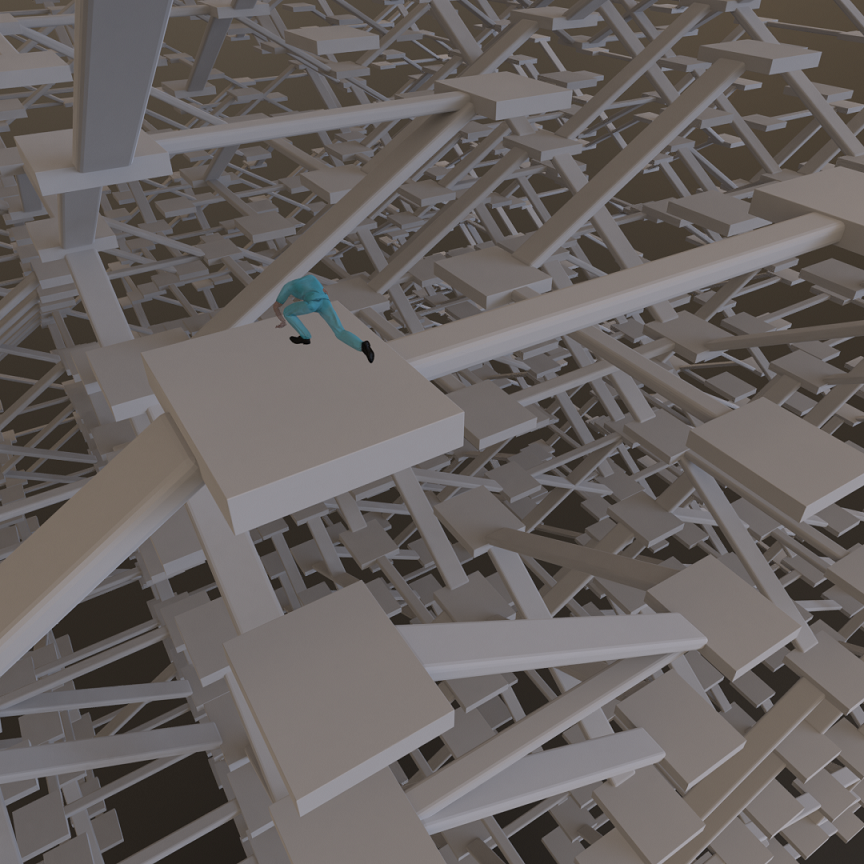
Sverchokで3D迷路を作成するという記事を見かけて、サンプルBlendファイルをダウンロードし開いてみたがうまく動かせなかった。
Scriptが使われておりScripted Nodeで動かすみたいだけど、2015年の記事で現行のSverchokでは既に動かなくなっていた。
という事で現代版で動かすべくScripted Node Liteについて調べてみた。
参照元
Script Node Lite(翻訳)
Scriptノードはさっくりと試せて、重要ではなく実験的なものを実行する事を意図しています。
ScriptNode MK1でできる多くの機能を実行できますが、いくつかの機能はサポートしていません。
※現行バージョンではScriptNode MK1自体が見当たらない
これらは issueセクションにリスト化されています。SN MK3と異なり、このノードはノードツリーの第一級市民になるような幻想は持っていません。更新ごとに少しのオーバーヘッドがあります。
正当化
私はSN1を気に入っていますが、ノードを事前処理・事前コンパイルする為だけに展開コードとインデックスコードを追加するのは好きではありません。
それらは決してビジョンの一部ではありませんでした。
コーダーの特権は自分の生活を可能な限り楽にする事です。時にそれはツールを作成する事に時間を費やすことを意味します。
SN lite は完璧ではありませんがSN MK3が熟成するまで私はこれでスクリプトを記述します。
特徴
- テンプレートをノードまたはテキストブロックへ直接インポートする事が簡単にできる(後者はテンプレートを読み込む前に変更するの有用です)
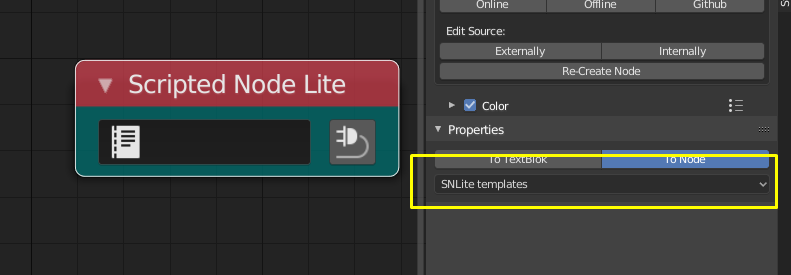
- 出力ソケットを強制しませんが、入力ソケットは期待しています(でなければどうやって更新する?!)
- いくつかのデフォルトを設定する事を許可しています: 数値、リストなど
- ネストのレベルを設定することを可能にしています; つまりコードを介した展開・インデックスのようなことは不要です。
- draw_buttonの上書きを宣言することを可能にしていますが、まぁ…drawコードへの追加と考えてください。マテリアルノードツリーのRGBカーブを使った軽量なカーブマッピングノードを作る方法の例があります。
- これはjavascriptが関数内の
argumentsで行うように変数参照のリストをパラメータとして自動で注入するオプションを持っています。本質的には次にように実装されています。
parameters = eval("[" + ", ".join([i.name for i in self.inputs]) + "]")Code language: PHP (php)この機能を有効にする為にヘッダーにinjectという単語を追加してください。もしradius, amplitude, num_vertsと呼ばれる入力ソケットがあるなら、変数 parameters は下記のようになります
parameters = [radius, amplitude, num_verts ]これは引数を正確にその順番で取るように配置された内部関数の場合に便利です。#942 (comment) に使用例があります。通常はvectorize関数を使って
引数のペアをzip化するでしょう。
- ヘルパ関数
from sverchok.utils.snlite_utils import vectorizeを追加しました。そしてこれは現在インポートする必要もありません。#942 (comment) を見てください - include命令文を追加しました
"""
...
include <your_text_name>
"""Code language: PHP (php)このinclude命令は依存関係がjsonとしてエクスポートされた時にgistにも保存される事を保証します。角括弧で指定されたファイルは、現在の .blend ファイルのテキストブロックの中に存在している必要があります。
– カスタムな描画を少し便利にするためにデフォルトのenumを追加しました。今の所カスタムなenumは1つだけで、デフォルトは”A”、”B”です。 self.custom_enumで呼び出します。要素間にスペースを入れてください。
"""
enum = word1 word2 word3
"""
Code language: PHP (php)- ローカルの名前空間に
ddirを追加。ddir(object, filter_str="some_string")filter_strはオプション。
def ddir(content, filter_str=None):
vals = []
if not filter_str:
vals = [n for n in dir(content) if not n.startswith('__')]
else:
vals = [n for n in dir(content) if not n.startswith('__') and filter_str in n]
return valsCode language: PHP (php)bmesh_from_pydataとpydata_from_bmeshをローカルに追加してインポートしなくていいようにしました- コールバックを追加しました。#942 (comment)を見てください
"""
in verts v
"""
def my_operator(self, context):
print(self, context, self.inputs['verts'].sv_get())
return {'FINISHED'}
self.make_operator('my_operator')
def ui(self, context, layout):
cb_str = 'node.scriptlite_custom_callback'
layout.operator(cb_str, text='show me').cb_name='my_operator'Code language: PHP (php)statefull(Processing のsetup()のような): importlibの例を見てください。- 再読み込みとインポート: importlibの例を見てください。これは特にsnliteのメインスクリプト外で定義するクラスのようなより複雑なコードで作業する時に有用です。
構文(Syntax)
構文はこのようになります
""" (tripple quote marks to demark the header)
in socketname type default=x nested=n
in socketname2 type default=x nested=n
out socketname type # (optional)
"""
< any python code >Code language: PHP (php)この3つのクォートのエリア(コメントまたはヘッダー)は .py ファイルの先頭にある必要があります。これはソケットの宣言や初期値使われ、特定のオプションを有効にする為のスペースです。上記の例のヘッダーはもう少し簡潔に書けます。
"""
in socketname type d=x n=i
in socketname2 type d=x n=i
out socketname type
"""
< any python code >Code language: PHP (php)気付いたいくつかの事
- 私は
defaultとnestedという単語を落としてdとnとしましたが、私が書いた例でin socketname type .=200 .=2のようなものも見るでしょう。dやnには何も意味がなく実質的な要件は=のすぐ左隣に任意の一文字がある事です。 - ソケット名はローカルスコープに注入されます。例えば
normalsという入力ソケットがある場合、normalsという変数から参照する事が出来ますedgesという出力ソケットがある場合、そちらも自動的に利用可能になります。SNLiteの背景としてコードを事項する前にedges_out = []を実行します。コードの終了部分で SNLiteはedges_outの内容がどうであれその内容をソケットの出力値として使います。
inputs
direction socketname sockettype default nestedness in radius s .=1.2 .=2
- direction
inは入力ソケットの作成を意味する - socketname はソケット名/識別子を意味する
- socket type はソケットの種類を宣言する
- Vertices (v)
- Strings/ Lists (s)
- Matrices (m)
- Curves (C)
- Surfaces (S)
- Scalar fields (SF)
- Vector fields (SF)
- Objects (o)
- default はデフォルト値を与える。リスト、タプル、整数など
- 注意: 反復するものにスペースを入れないでください。パースが中断されます
- nestedness について。 Sverchokのすべてのデータ構造は何らかの方法でネストされています。これを理解するにはpythonやサブリストの概念をある程度理解している必要があります。使うよりも説明のほうが難しいです。
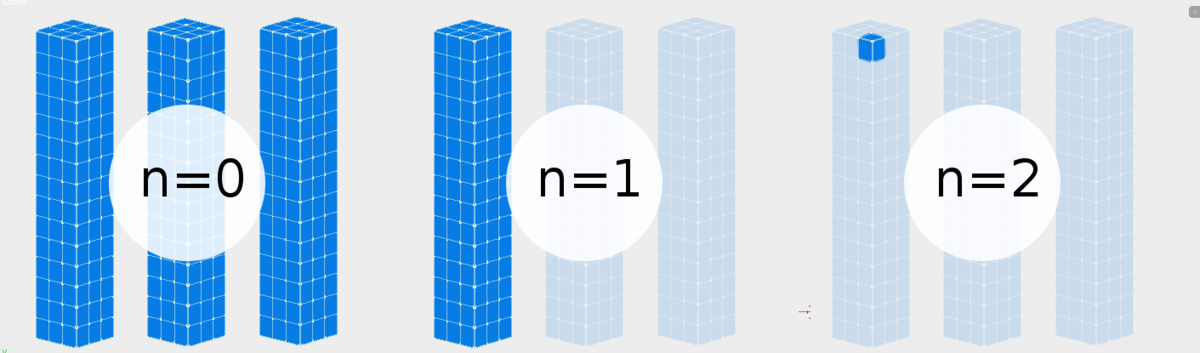
n=2はnamed_input.sv_get()[0][0]を意味しています- これはあなたが単一の値が欲しいことを意味しています
named_input = [[20, 30, 40], .....] # or [[20]]value_to_use = named_input[0][0] # 20
“`
n=1はnamed_input.sv_get()[0]を意味しています- 最初に入ってくるサブリストだけで作業をすることにしているなら
n=1を使います
- 最初に入ってくるサブリストだけで作業をすることにしているなら
n=0はnamed_input.sv_get()を意味します- 一般的にこれを使うのは入力されるそれぞれのサブリストで作業をする場合です。例えば、入力がいくつかの頂点を持っている場合。

- 一般的にこれを使うのは入力されるそれぞれのサブリストで作業をする場合です。例えば、入力がいくつかの頂点を持っている場合。
outputs:
direction socketname sockettype out verts v
- direction
inは出力ソケットの作成を意味する - socketname はソケット名/識別子を意味する
- sockettype は入力と同様
出力ソケットではdefaultやnestedがありません。一般的に言えばデフォルト値がデフォルト出力値を生成するのに十分です。
例から学びましょう、それが
どのように動き、動かないかを理解する最も良い方法です。
- #942
node_scripts/SNLite_templatesdraw_buttons_ext(NodeView のプロパティ)
テンプレートは防御力の高いコードはそんなにありません、あるノードは入力を期待していてソケットから入力されるまで赤くなります。あなたはコードを追加してこれを防げますが、私は予期せぬ入力があった場合、ノードが潔く失敗することを素早く通知してくれるのは便利だと感じています。
翻訳終わり。
後は参照元には色々サンプルがあるので興味のある方は見てみてください
最初に戻って3D迷路のファイルを見る
上記のページでは3D迷路を作成する為のblendファイルへのリンクがある。
そしてファイルには迷路を作るためのスクリプトが含まれている
maze_3d.py の内容をざっと見る限り、sverchokで影響しそうな箇所はなかった。
そして maze_passage_3D.py には sverchokで影響しそうな箇所がいくつかあったのでそちらを修正した。
ソース
maze_passage_3D.py
"""
in rseed s d=21 n=0
in sizeX s d=4 n=0
in sizeY s d=4 n=0
in sizeZ s d=4 n=0
in scaleXY s d=1.0 n=0
in scaleZ s d=1.0 n=0
in braid s d=0.0 n=0
out matrices m
out mask s
"""
"""
Sverchok scripted node for simple 2D maze generation
elfnor.com 2015
maze library by Sami Salkosuo
gist.github.com/samisalkosuo/77bd95f605fc41dc7366
following "Mazes for Programmers"
https://pragprog.com/book/jbmaze/mazes-for-programmers
"""
import mathutils as mu
from sverchok.data_structure import Matrix_listing
import os
import sys
import bpy
dir = os.path.dirname(bpy.data.filepath)
if not dir in sys.path:
sys.path.append(dir )
#print(sys.path)
import maze_3d
from math import pi
pathDict = {'north': (pi, 5, 0.0, 1),
'east': (pi/2.0, 5, pi/2.0, 1),
'south': (0.0, 5, 0.0, 1),
'west' : (3.0*pi/2.0, 5, 3.0 * pi/2.0, 1),
'northUp': (pi, 6, pi, 2),
'eastUp' : (pi/2.0, 6, pi/2.0, 2),
'southUp': (0.0, 6, 0.0, 2),
'westUp': (3.0*pi/2.0, 6, 3.0*pi/2.0, 2),
'northDown': (pi, 7, 0.0, 2),
'eastDown': (pi/2.0, 7, 3.0*pi/2.0, 2 ),
'southDown': (0.0, 7, pi, 2),
'westDown' : (3.0*pi/2.0, 7, pi/2.0, 2 )}
class SvGrid(maze_3d.Grid3dDiag):
def pathMatrices(self):
"""
outputs: list of mathutils Matrix mats
list of integers mask
mats: location and orientation of maze path tiles
mask: which type of path tile to place
"""
mats = []
mask = []
# platform matrices
for cell in self.eachCell():
m = mu.Matrix.Identity(4)
m[0][3] = cell.row
m[1][3] = cell.column
m[2][3] = cell.level
mats.append(m)
mask.append(0)
# links matrices
for cell, dirn, typeID in self.eachEdge():
# need a lookup table for all combinations of dirn and type ID
if typeID == 2:
#edge
zrot = pathDict[dirn][0]
m = mu.Matrix.Rotation(zrot, 4, 'Z')
m[0][3] = cell.row
m[1][3] = cell.column
m[2][3] = cell.level
mats.append(m)
mask.append(pathDict[dirn][1])
else:
#internal path or gap
zrot = pathDict[dirn][2]
m = mu.Matrix.Rotation(zrot, 4, 'Z')
m[0][3] = cell.row + 0.5 * cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1]
m[1][3] = cell.column + 0.5 * cell.neighborDirns[dirn][2]
m[2][3] = cell.level + 0.5 * cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0]
mats.append(m)
if typeID == 0:
mask.append(pathDict[dirn][3])
else:
mask.append(pathDict[dirn][3] + 2)
return mats, mask
maze_3d.random.seed(rseed)
grid=SvGrid(sizeZ, sizeX, sizeY)
grid=maze_3d.initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid)
grid.braid(braid)
#print(grid)
mats, mask = grid.pathMatrices()
#scale locations
for m in mats:
for i in range(2):
m[i][3] = m[i][3] * scaleXY
m[2][3] = m[2][3] * scaleZ
matrices = mats修正箇所
- input, output をヘッダー部分へ移動
- sv_main という関数の内容をグローバルスコープへ移動し関数は削除
- Matrix_listing は使わないように変更。これがあるとDraw Viewer からは使えてもBMesh Viewer からは使用できなくなるため
- ファイルが保存されているディレクトリのpyスクリプトをimportするようにコードを追加
- include ディレクティブを使いたかったが、includeディレクティブはsverchokアドオンのディレクトリ内を参照するようなので今回はパス
特に修正していないが maze_3d.py のソースも載せておく。
maze_3d.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# started as gist from https://gist.github.com/samisalkosuo/77bd95f605fc41dc7366
# adapted for use in Blender Sverchok
# 3D diagonal classes added
#Some mazes classes translated from Ruby
#from book "Mazes for Programmers" by Jamis Buck.
#https://pragprog.com/book/jbmaze/mazes-for-programmers
import random
class Cell:
def __init__(self,row,column):
self.row=row
self.column=column
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys, ((-1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1))))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
self.links=dict()
def link(self,cell,bidi=True):
self.links[cell] = True
if bidi==True:
cell.link(self,False)
return self
def unlink(self,cell,bidi=True):
try:
del self.links[cell]
except KeyError:
pass
if bidi==True:
cell.unlink(self, False)
return self
def getLinks(self):
return self.links.keys()
def linked(self,cell):
return cell in self.links
def neighbors(self):
"""
returns list of neighbors that exist
"""
neighborList = [cell for k, cell in self.neighborDict.items() if cell]
return neighborList
def getDistances(self):
distances=Distances(self)
frontier=[]
frontier.append(self)
while len(frontier)>0:
newFrontier=[]
for cell in frontier:
for linked in cell.getLinks():
if distances.getDistanceTo(linked) is None:
dist=distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
distances.setDistanceTo(linked,dist+1)
newFrontier.append(linked)
frontier=newFrontier
return distances
def linkedID(self):
"""
returns an integer representing which neighbors are linked
this is binary, self.neighborKeys[0] is LSB
self.neighborKeys[-1] is MSB
"""
ngh = [self.linked(self.neighborDict[dirn]) for dirn in self.neighborKeys ]
nghID = sum( 2**i*b for i, b in enumerate(ngh))
return nghID
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d,%d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Distances:
def __init__(self,rootCell):
self.rootCell=rootCell
self.cells=dict()
self.cells[self.rootCell]=0
def getDistanceTo(self,cell):
return self.cells.get(cell,None)
def setDistanceTo(self,cell,distance):
self.cells[cell]=distance
def getCells(self):
return self.cells.keys()
def isPartOfPath(self,cell):
return self.cells.has_key(cell)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.cells.keys())
def pathTo(self,goal):
current=goal
breadcrumbs = Distances(self.rootCell)
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(current,self.cells[current])
while current is not self.rootCell:
for neighbor in current.getLinks():
if self.cells[neighbor] < self.cells[current]:
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(neighbor,self.cells[neighbor])
current=neighbor
break
return breadcrumbs
class Grid:
def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
self.CellClass=cellClass
self.rows=rows
self.columns=columns
self.grid=self.prepareGrid()
self.distances=None
self.configureCells()
def prepareGrid(self):
rowList=[]
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(i,j))
rowList.append(columnList)
return rowList
def eachRow(self):
for row in self.grid:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for row in self.grid:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def configureCells(self):
for cell in self.eachCell():
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1])
def getCell(self,row,column):
return self.grid[row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,row,column):
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[row][column]
def size(self):
return self.rows*self.columns
def randomCell(self):
row=random.randint(0, self.rows-1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[row][column]
def contentsOf(self,cell):
return " "
def __str__(self):
return self.asciiStr()
def unicodeStr(self):
pass
def asciiStr(self):
output = "+" + "---+" * self.columns + "\n"
for row in self.eachRow():
top = "|"
bottom = "+"
for cell in row:
if not cell:
cell=Cell(-1,-1)
body = "%s" % self.contentsOf(cell)
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['east']):
east_boundary=" "
else:
east_boundary="|"
top = top+ body + east_boundary
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['south']):
south_boundary=" "
else:
south_boundary="---"
corner = "+"
bottom =bottom+ south_boundary+ corner
output=output+top+"\n"
output=output+bottom+"\n"
return output
def deadends(self):
"""
returns a list of maze deadends
"""
ends = [cell for cell in self.eachCell() if len(cell.links) == 1 ]
return ends
def braid(self, p=1.0):
"""
Add links between dead ends (only one neighbour) and a neighbouring cell
p is the proportion (approx) of dead ends that are culled. Default p=1.0 removes
them all.
Linkind dead ends produces loops in the maze.
Prefers to link to another dead end if possible
"""
random.shuffle(self.deadends())
for cell in self.deadends():
if (len(cell.links) == 1) and (random.random() < p):
#its still a dead end, ignore some if p < 1
# find neighbours not linked to cell
unlinked = [ngh for ngh in cell.neighbors() if not(cell.linked(ngh))]
#find unlinked neighbours that are also dead ends
best = [ngh for ngh in unlinked if len(ngh.links) == 1]
if len(best) == 0:
best = unlinked
ngh = random.choice(best)
cell.link(ngh)
class DistanceGrid(Grid):
#def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
# super(Grid, self).__init__(rows,columns,cellClass)
def contentsOf(self,cell):
if self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None and self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None:
n=self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
return "%03d" % n
else:
return " " #super(Grid, self).contentsOf(cell)
## 3D maze neighbours are defined as
# 4 cells on same level,
# 4 cells above
# 4 cells below
class Cell3dDiag(Cell):
def __init__(self, level, row, column):
self.level = level
Cell.__init__(self, row, column)
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west',
'northUp', 'eastUp', 'southUp', 'westUp',
'northDown', 'eastDown', 'southDown', 'westDown')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys,
((0,-1, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, -1),
(1,-1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, -1),
(-1,-1, 0), (-1, 0, 1), (-1, 1, 0), (-1, 0, -1) )))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d, %d, %d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.level, self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Grid3dDiag(Grid):
def __init__(self, levels, rows, columns):
self.levels = levels
Grid.__init__(self, rows, columns, cellClass = Cell3dDiag)
def prepareGrid(self):
"""
grid is a triple nested list of cells
"""
levelList=[]
for h in range(self.levels):
rowList = []
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(h, i, j))
rowList.append(columnList)
levelList.append(rowList)
return levelList
def eachLevel(self):
for level in self,grid:
yield level
def eachRow(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def getCell(self,level, row, column):
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,level, row, column):
"""
defines borders by returning None outside grid
"""
if not (0 <= level < self.levels):
return None
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def configureCells(self):
"""
set up neighbours, defines edges
"""
for cell in self.eachCell():
level = cell.level
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(
level + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][2])
def size(self):
return self.columns * self.rows * self.columns
def randomCell(self):
level = random.randint(0, self.levels - 1)
row = random.randint(0, self.rows - 1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def eachEdge(self):
"""
generator thst yields each potential path only once
yields (cell, direction, type)
where type 0 is a link, type is no link and type 3
is on the edge of the maze, that is cell has no neighbor
"""
seen = set()
for i, cell in enumerate(self.eachCell()):
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
if cell.neighborDict[dirn]:
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict[dirn]):
typeID = 0
else:
typeID = 1
celln = cell.neighborDict[dirn]
neighbor_i = celln.level*self.rows*self.columns + celln.row*self.columns + celln.column
ekey = [i, neighbor_i]
ekey.sort()
ekey = tuple(ekey)
#print(seen)
if ekey not in seen:
seen.add(ekey)
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
else:
typeID = 2
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
## carving functions
def initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid):
stack = []
stack.append(grid.randomCell())
while len(stack)>0:
current = stack[-1]
neighbors=[]
for n in current.neighbors():
if len(n.getLinks())==0:
neighbors.append(n)
if len(neighbors)==0:
stack.pop()
else:
neighbor = random.choice(neighbors)
current.link(neighbor)
stack.append(neighbor)
return grid
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid=Grid3dDiag(4, 4, 4)
#grid = Grid(10,10)
grid=initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid)
print(grid.size())
#print(grid)#!/usr/bin/env python
# started as gist from https://gist.github.com/samisalkosuo/77bd95f605fc41dc7366
# adapted for use in Blender Sverchok
# 3D diagonal classes added
#Some mazes classes translated from Ruby
#from book "Mazes for Programmers" by Jamis Buck.
#https://pragprog.com/book/jbmaze/mazes-for-programmers
import random
class Cell:
def __init__(self,row,column):
self.row=row
self.column=column
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys, ((-1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1))))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
self.links=dict()
def link(self,cell,bidi=True):
self.links[cell] = True
if bidi==True:
cell.link(self,False)
return self
def unlink(self,cell,bidi=True):
try:
del self.links[cell]
except KeyError:
pass
if bidi==True:
cell.unlink(self, False)
return self
def getLinks(self):
return self.links.keys()
def linked(self,cell):
return cell in self.links
def neighbors(self):
"""
returns list of neighbors that exist
"""
neighborList = [cell for k, cell in self.neighborDict.items() if cell]
return neighborList
def getDistances(self):
distances=Distances(self)
frontier=[]
frontier.append(self)
while len(frontier)>0:
newFrontier=[]
for cell in frontier:
for linked in cell.getLinks():
if distances.getDistanceTo(linked) is None:
dist=distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
distances.setDistanceTo(linked,dist+1)
newFrontier.append(linked)
frontier=newFrontier
return distances
def linkedID(self):
"""
returns an integer representing which neighbors are linked
this is binary, self.neighborKeys[0] is LSB
self.neighborKeys[-1] is MSB
"""
ngh = [self.linked(self.neighborDict[dirn]) for dirn in self.neighborKeys ]
nghID = sum( 2**i*b for i, b in enumerate(ngh))
return nghID
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d,%d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Distances:
def __init__(self,rootCell):
self.rootCell=rootCell
self.cells=dict()
self.cells[self.rootCell]=0
def getDistanceTo(self,cell):
return self.cells.get(cell,None)
def setDistanceTo(self,cell,distance):
self.cells[cell]=distance
def getCells(self):
return self.cells.keys()
def isPartOfPath(self,cell):
return self.cells.has_key(cell)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.cells.keys())
def pathTo(self,goal):
current=goal
breadcrumbs = Distances(self.rootCell)
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(current,self.cells[current])
while current is not self.rootCell:
for neighbor in current.getLinks():
if self.cells[neighbor] < self.cells[current]:
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(neighbor,self.cells[neighbor])
current=neighbor
break
return breadcrumbs
class Grid:
def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
self.CellClass=cellClass
self.rows=rows
self.columns=columns
self.grid=self.prepareGrid()
self.distances=None
self.configureCells()
def prepareGrid(self):
rowList=[]
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(i,j))
rowList.append(columnList)
return rowList
def eachRow(self):
for row in self.grid:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for row in self.grid:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def configureCells(self):
for cell in self.eachCell():
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1])
def getCell(self,row,column):
return self.grid[row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,row,column):
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[row][column]
def size(self):
return self.rows*self.columns
def randomCell(self):
row=random.randint(0, self.rows-1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[row][column]
def contentsOf(self,cell):
return " "
def __str__(self):
return self.asciiStr()
def unicodeStr(self):
pass
def asciiStr(self):
output = "+" + "---+" * self.columns + "\n"
for row in self.eachRow():
top = "|"
bottom = "+"
for cell in row:
if not cell:
cell=Cell(-1,-1)
body = "%s" % self.contentsOf(cell)
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['east']):
east_boundary=" "
else:
east_boundary="|"
top = top+ body + east_boundary
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['south']):
south_boundary=" "
else:
south_boundary="---"
corner = "+"
bottom =bottom+ south_boundary+ corner
output=output+top+"\n"
output=output+bottom+"\n"
return output
def deadends(self):
"""
returns a list of maze deadends
"""
ends = [cell for cell in self.eachCell() if len(cell.links) == 1 ]
return ends
def braid(self, p=1.0):
"""
Add links between dead ends (only one neighbour) and a neighbouring cell
p is the proportion (approx) of dead ends that are culled. Default p=1.0 removes
them all.
Linkind dead ends produces loops in the maze.
Prefers to link to another dead end if possible
"""
random.shuffle(self.deadends())
for cell in self.deadends():
if (len(cell.links) == 1) and (random.random() < p):
#its still a dead end, ignore some if p < 1
# find neighbours not linked to cell
unlinked = [ngh for ngh in cell.neighbors() if not(cell.linked(ngh))]
#find unlinked neighbours that are also dead ends
best = [ngh for ngh in unlinked if len(ngh.links) == 1]
if len(best) == 0:
best = unlinked
ngh = random.choice(best)
cell.link(ngh)
class DistanceGrid(Grid):
#def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
# super(Grid, self).__init__(rows,columns,cellClass)
def contentsOf(self,cell):
if self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None and self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None:
n=self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
return "%03d" % n
else:
return " " #super(Grid, self).contentsOf(cell)
## 3D maze neighbours are defined as
# 4 cells on same level,
# 4 cells above
# 4 cells below
class Cell3dDiag(Cell):
def __init__(self, level, row, column):
self.level = level
Cell.__init__(self, row, column)
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west',
'northUp', 'eastUp', 'southUp', 'westUp',
'northDown', 'eastDown', 'southDown', 'westDown')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys,
((0,-1, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, -1),
(1,-1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, -1),
(-1,-1, 0), (-1, 0, 1), (-1, 1, 0), (-1, 0, -1) )))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d, %d, %d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.level, self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Grid3dDiag(Grid):
def __init__(self, levels, rows, columns):
self.levels = levels
Grid.__init__(self, rows, columns, cellClass = Cell3dDiag)
def prepareGrid(self):
"""
grid is a triple nested list of cells
"""
levelList=[]
for h in range(self.levels):
rowList = []
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(h, i, j))
rowList.append(columnList)
levelList.append(rowList)
return levelList
def eachLevel(self):
for level in self,grid:
yield level
def eachRow(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def getCell(self,level, row, column):
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,level, row, column):
"""
defines borders by returning None outside grid
"""
if not (0 <= level < self.levels):
return None
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def configureCells(self):
"""
set up neighbours, defines edges
"""
for cell in self.eachCell():
level = cell.level
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(
level + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][2])
def size(self):
return self.columns * self.rows * self.columns
def randomCell(self):
level = random.randint(0, self.levels - 1)
row = random.randint(0, self.rows - 1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def eachEdge(self):
"""
generator thst yields each potential path only once
yields (cell, direction, type)
where type 0 is a link, type is no link and type 3
is on the edge of the maze, that is cell has no neighbor
"""
seen = set()
for i, cell in enumerate(self.eachCell()):
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
if cell.neighborDict[dirn]:
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict[dirn]):
typeID = 0
else:
typeID = 1
celln = cell.neighborDict[dirn]
neighbor_i = celln.level*self.rows*self.columns + celln.row*self.columns + celln.column
ekey = [i, neighbor_i]
ekey.sort()
ekey = tuple(ekey)
#print(seen)
if ekey not in seen:
seen.add(ekey)
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
else:
typeID = 2
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
## carving functions
def initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid):
stack = []
stack.append(grid.randomCell())
while len(stack)>0:
current = stack[-1]
neighbors=[]
for n in current.neighbors():
if len(n.getLinks())==0:
neighbors.append(n)
if len(neighbors)==0:
stack.pop()
else:
neighbor = random.choice(neighbors)
current.link(neighbor)
stack.append(neighbor)
return grid
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid=Grid3dDiag(4, 4, 4)
#grid = Grid(10,10)
grid=initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid)
print(grid.size())
#print(grid)
```#!/usr/bin/env python
# started as gist from https://gist.github.com/samisalkosuo/77bd95f605fc41dc7366
# adapted for use in Blender Sverchok
# 3D diagonal classes added
#Some mazes classes translated from Ruby
#from book "Mazes for Programmers" by Jamis Buck.
#https://pragprog.com/book/jbmaze/mazes-for-programmers
import random
class Cell:
def __init__(self,row,column):
self.row=row
self.column=column
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys, ((-1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1))))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
self.links=dict()
def link(self,cell,bidi=True):
self.links[cell] = True
if bidi==True:
cell.link(self,False)
return self
def unlink(self,cell,bidi=True):
try:
del self.links[cell]
except KeyError:
pass
if bidi==True:
cell.unlink(self, False)
return self
def getLinks(self):
return self.links.keys()
def linked(self,cell):
return cell in self.links
def neighbors(self):
"""
returns list of neighbors that exist
"""
neighborList = [cell for k, cell in self.neighborDict.items() if cell]
return neighborList
def getDistances(self):
distances=Distances(self)
frontier=[]
frontier.append(self)
while len(frontier)>0:
newFrontier=[]
for cell in frontier:
for linked in cell.getLinks():
if distances.getDistanceTo(linked) is None:
dist=distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
distances.setDistanceTo(linked,dist+1)
newFrontier.append(linked)
frontier=newFrontier
return distances
def linkedID(self):
"""
returns an integer representing which neighbors are linked
this is binary, self.neighborKeys[0] is LSB
self.neighborKeys[-1] is MSB
"""
ngh = [self.linked(self.neighborDict[dirn]) for dirn in self.neighborKeys ]
nghID = sum( 2**i*b for i, b in enumerate(ngh))
return nghID
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d,%d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Distances:
def __init__(self,rootCell):
self.rootCell=rootCell
self.cells=dict()
self.cells[self.rootCell]=0
def getDistanceTo(self,cell):
return self.cells.get(cell,None)
def setDistanceTo(self,cell,distance):
self.cells[cell]=distance
def getCells(self):
return self.cells.keys()
def isPartOfPath(self,cell):
return self.cells.has_key(cell)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.cells.keys())
def pathTo(self,goal):
current=goal
breadcrumbs = Distances(self.rootCell)
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(current,self.cells[current])
while current is not self.rootCell:
for neighbor in current.getLinks():
if self.cells[neighbor] < self.cells[current]:
breadcrumbs.setDistanceTo(neighbor,self.cells[neighbor])
current=neighbor
break
return breadcrumbs
class Grid:
def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
self.CellClass=cellClass
self.rows=rows
self.columns=columns
self.grid=self.prepareGrid()
self.distances=None
self.configureCells()
def prepareGrid(self):
rowList=[]
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(i,j))
rowList.append(columnList)
return rowList
def eachRow(self):
for row in self.grid:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for row in self.grid:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def configureCells(self):
for cell in self.eachCell():
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1])
def getCell(self,row,column):
return self.grid[row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,row,column):
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[row][column]
def size(self):
return self.rows*self.columns
def randomCell(self):
row=random.randint(0, self.rows-1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[row][column]
def contentsOf(self,cell):
return " "
def __str__(self):
return self.asciiStr()
def unicodeStr(self):
pass
def asciiStr(self):
output = "+" + "---+" * self.columns + "\n"
for row in self.eachRow():
top = "|"
bottom = "+"
for cell in row:
if not cell:
cell=Cell(-1,-1)
body = "%s" % self.contentsOf(cell)
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['east']):
east_boundary=" "
else:
east_boundary="|"
top = top+ body + east_boundary
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict['south']):
south_boundary=" "
else:
south_boundary="---"
corner = "+"
bottom =bottom+ south_boundary+ corner
output=output+top+"\n"
output=output+bottom+"\n"
return output
def deadends(self):
"""
returns a list of maze deadends
"""
ends = [cell for cell in self.eachCell() if len(cell.links) == 1 ]
return ends
def braid(self, p=1.0):
"""
Add links between dead ends (only one neighbour) and a neighbouring cell
p is the proportion (approx) of dead ends that are culled. Default p=1.0 removes
them all.
Linkind dead ends produces loops in the maze.
Prefers to link to another dead end if possible
"""
random.shuffle(self.deadends())
for cell in self.deadends():
if (len(cell.links) == 1) and (random.random() < p):
#its still a dead end, ignore some if p < 1
# find neighbours not linked to cell
unlinked = [ngh for ngh in cell.neighbors() if not(cell.linked(ngh))]
#find unlinked neighbours that are also dead ends
best = [ngh for ngh in unlinked if len(ngh.links) == 1]
if len(best) == 0:
best = unlinked
ngh = random.choice(best)
cell.link(ngh)
class DistanceGrid(Grid):
#def __init__(self,rows,columns,cellClass=Cell):
# super(Grid, self).__init__(rows,columns,cellClass)
def contentsOf(self,cell):
if self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None and self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell) is not None:
n=self.distances.getDistanceTo(cell)
return "%03d" % n
else:
return " " #super(Grid, self).contentsOf(cell)
## 3D maze neighbours are defined as
# 4 cells on same level,
# 4 cells above
# 4 cells below
class Cell3dDiag(Cell):
def __init__(self, level, row, column):
self.level = level
Cell.__init__(self, row, column)
self.neighborKeys = ('north', 'east', 'south', 'west',
'northUp', 'eastUp', 'southUp', 'westUp',
'northDown', 'eastDown', 'southDown', 'westDown')
self.neighborDirns = dict(zip(self.neighborKeys,
((0,-1, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, -1),
(1,-1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, -1),
(-1,-1, 0), (-1, 0, 1), (-1, 1, 0), (-1, 0, -1) )))
self.neighborDict = dict.fromkeys(self.neighborKeys)
def __str__(self):
nghID = self.linkedID()
output="Cell[%d, %d, %d], Linked neighbors ID:%d " % (self.level, self.row,self.column, nghID)
return output
class Grid3dDiag(Grid):
def __init__(self, levels, rows, columns):
self.levels = levels
Grid.__init__(self, rows, columns, cellClass = Cell3dDiag)
def prepareGrid(self):
"""
grid is a triple nested list of cells
"""
levelList=[]
for h in range(self.levels):
rowList = []
for i in range(self.rows):
columnList=[]
for j in range(self.columns):
columnList.append(self.CellClass(h, i, j))
rowList.append(columnList)
levelList.append(rowList)
return levelList
def eachLevel(self):
for level in self,grid:
yield level
def eachRow(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
yield row
def eachCell(self):
for level in self.grid:
for row in level:
for cell in row:
yield cell
def getCell(self,level, row, column):
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def getNeighbor(self,level, row, column):
"""
defines borders by returning None outside grid
"""
if not (0 <= level < self.levels):
return None
if not (0 <= row < self.rows):
return None
if not (0 <= column < self.columns):
return None
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def configureCells(self):
"""
set up neighbours, defines edges
"""
for cell in self.eachCell():
level = cell.level
row=cell.row
col=cell.column
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
cell.neighborDict[dirn] = self.getNeighbor(
level + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][0],
row + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][1],
col + cell.neighborDirns[dirn][2])
def size(self):
return self.columns * self.rows * self.columns
def randomCell(self):
level = random.randint(0, self.levels - 1)
row = random.randint(0, self.rows - 1)
column = random.randint(0, self.columns - 1)
return self.grid[level][row][column]
def eachEdge(self):
"""
generator thst yields each potential path only once
yields (cell, direction, type)
where type 0 is a link, type is no link and type 3
is on the edge of the maze, that is cell has no neighbor
"""
seen = set()
for i, cell in enumerate(self.eachCell()):
for dirn in cell.neighborDirns:
if cell.neighborDict[dirn]:
if cell.linked(cell.neighborDict[dirn]):
typeID = 0
else:
typeID = 1
celln = cell.neighborDict[dirn]
neighbor_i = celln.level*self.rows*self.columns + celln.row*self.columns + celln.column
ekey = [i, neighbor_i]
ekey.sort()
ekey = tuple(ekey)
#print(seen)
if ekey not in seen:
seen.add(ekey)
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
else:
typeID = 2
yield (cell, dirn, typeID)
## carving functions
def initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid):
stack = []
stack.append(grid.randomCell())
while len(stack)>0:
current = stack[-1]
neighbors=[]
for n in current.neighbors():
if len(n.getLinks())==0:
neighbors.append(n)
if len(neighbors)==0:
stack.pop()
else:
neighbor = random.choice(neighbors)
current.link(neighbor)
stack.append(neighbor)
return grid
if __name__ == "__main__":
grid=Grid3dDiag(4, 4, 4)
#grid = Grid(10,10)
grid=initRecursiveBacktrackerMaze(grid)
print(grid.size())
#print(grid)使用手順
- Text Editor からmaze_passage_3D.pyを開く
- maze_3d.py はblendファイルが保存されているディレクトリに保存しておく
- Generator -> Script Node Lite を配置し、maze_passage_3D.py を指定する
- 指定後はコンセントのマークをクリックすれば読み込まれる
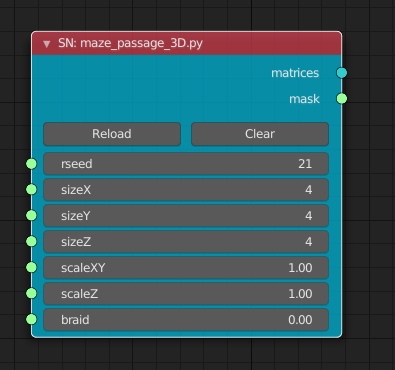
- rseed は乱数生成のシード
- sizeX、sizeY、sizeZはそれぞれの次元数
- scaleXY はXY間の幅
- scaleZ は各層の幅
- braid は迷路内の行き止まりとループの割合を設定。0にすると行き止まりがあり、ループはない。1に設定するとループが多く行き止まりは無い。
ノーディング
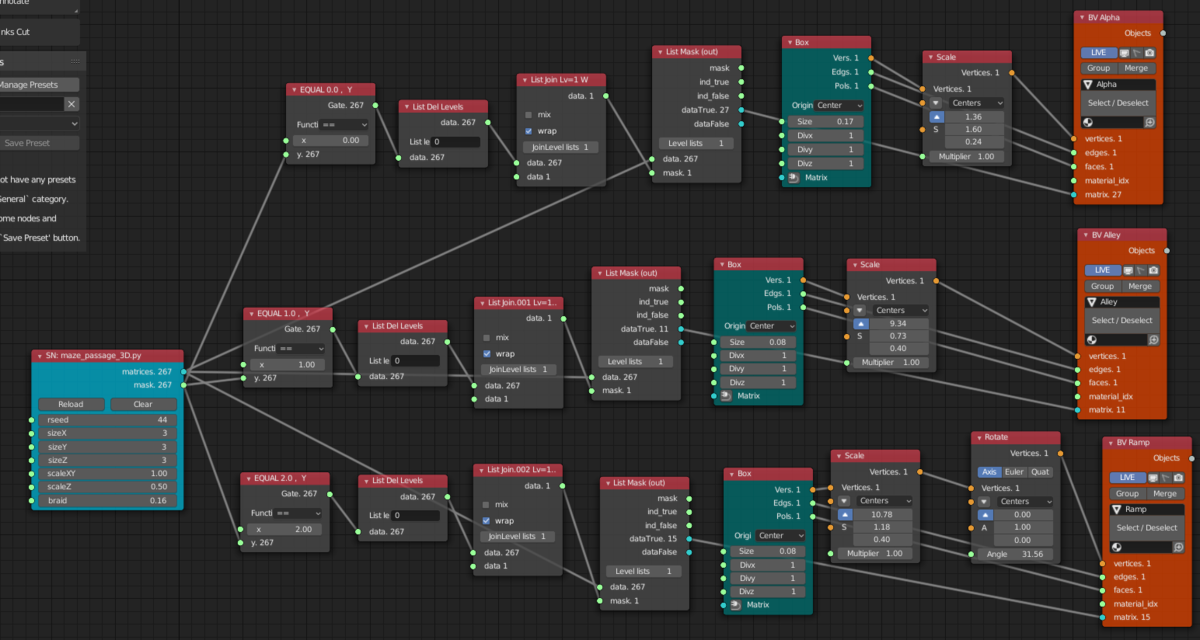
- script ノードは2つの出力がある。1つは座標と回転が定義された行列で、もう一つはその行列が何を表しているかを示すMask
- 行列が表すもの(Maskに保存されている数値)
- 0 platform 踊り場
- 1 bridge 橋(左右前後の踊り場を接続)
- 2 ramp 坂(上下の層を接続)
- 3 ~ 7 は手すりなどに使うみたい
- 右端にある3つのBMesh Viewerは上から踊り場、橋、坂となっている
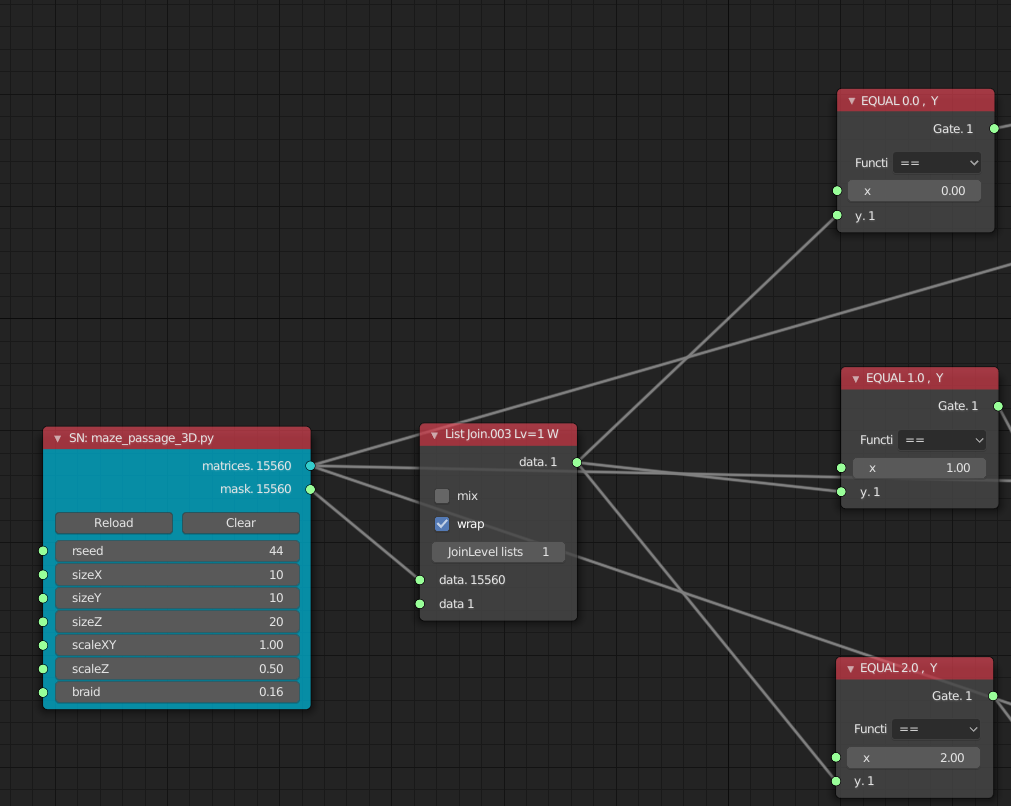
- 1段目の解説
- Mask からの出力で 0 に等しいものは踊り場のため、Logic Function の == で0に等しいか確認している
- Logic Function の結果は
[[True], [False], ... , [True]]のような2次元配列となるが、ほしいのは[[True, False, ..., True]]のような2次元配列のため、List Del Levels と List Joinでそのような形のリストに変換している - List Mask (out) で Maskされたデータのみを抽出している
- Box は踊り場となる Box で Scale で平べったくしている
- BMesh Viewer でオブジェクト化
- 2段目、3段目もほぼ同様のことを行っている。3段目のみ坂のため坂となるように板を回転している
Sverchok 2020/4/21からは更に Logic Function の手前でList Joinをしないと動かないようです。上記の通りやっても動かない場合はLogic Functionの手前でList Joinを追加してください
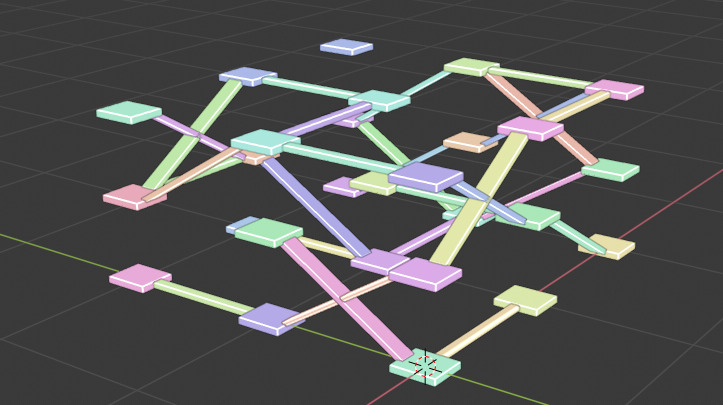
結果
最後に
プログラミングは少しできるものの本格的なものとなると尻込みするレベルなので、書いている内容の半分くらいわからなかった。あと、迷路3Dのソースは難しくて修正するためにMatrix in のソースまで参照した。ほんの少しレベルが上がった気がしたので結果オーライ。3Dマスターへの道のりは長い